The Real Impact of Window Ratings on Your Home
Choosing the right windows significantly impacts your home's energy efficiency and comfort. Many homeowners underestimate the role windows play in their energy bills and overall comfort. However, consultations with energy auditors and industry experts highlight a crucial point: window efficiency is paramount for both monthly expenses and daily living.
Even minor improvements in window energy efficiency ratings can yield substantial benefits, particularly during seasonal temperature fluctuations. For instance, a small increase in insulation can noticeably reduce heating bills in the winter and cooling costs in the summer. This means investing in energy-efficient windows provides year-round advantages. Furthermore, these improvements contribute to a more stable indoor temperature, minimizing drafts and uncomfortable hot spots.
The impact of window upgrades becomes strikingly clear when examining real-world scenarios. Homes with new windows often report significantly improved temperature stability. This translates to a more comfortable living environment and, crucially, lower utility expenses. In fact, studies reveal that windows contribute significantly to residential energy loss. Windows account for approximately 25% to 30% of residential heating and cooling energy use in the United States, totaling roughly 2.5 quadrillion Btu each year. Upgrading to ENERGY STAR certified windows can lower annual energy costs by up to 15%, resulting in savings between USD 71 and USD 105. Learn more about window efficiency's impact on energy consumption here: Impact of Window Efficiency
How Window Efficiency Improves Comfort and Savings
The advantages of energy-efficient windows go beyond mere cost savings. They create a healthier and more pleasant living space.
-
Reduced Drafts: Well-sealed and insulated windows minimize drafts, eliminating chilly areas near windows during winter.
-
Noise Reduction: Many energy-efficient windows provide enhanced sound insulation, decreasing outside noise for a more tranquil indoor environment.
-
Less Condensation: Improved insulation helps prevent condensation buildup on windows, reducing the likelihood of mold and mildew growth.
-
Protection for Furnishings: Energy-efficient windows can block harmful UV rays that can fade furniture, carpets, and artwork over time.
The right window features can address specific home design issues and regional climate factors. For example, homes in warmer climates benefit from windows with low solar heat gain coefficients (SHGC), while homes in colder climates should prioritize low U-factors for enhanced insulation. Choosing windows appropriate for your climate ensures optimal performance and maximum energy savings.
Cracking the Code: Window Rating Labels Demystified
Understanding window energy efficiency ratings is crucial for making informed decisions, whether you're planning a renovation or building a new home. While these ratings might seem technical, they provide valuable insights into a window's performance. This guide will break down the jargon into practical knowledge, empowering you to compare options effectively and avoid common purchasing pitfalls.
Understanding U-Factor and SHGC
Two key metrics dominate window energy efficiency ratings: the U-factor and the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). The U-factor measures how well a window prevents heat loss. Think of it as insulation – the lower the U-factor, the better the window retains heat, much like a warm winter coat. The SHGC, on the other hand, measures how much solar heat passes through the glass. A lower SHGC is desirable in warmer climates to minimize heat gain and keep interiors cool.
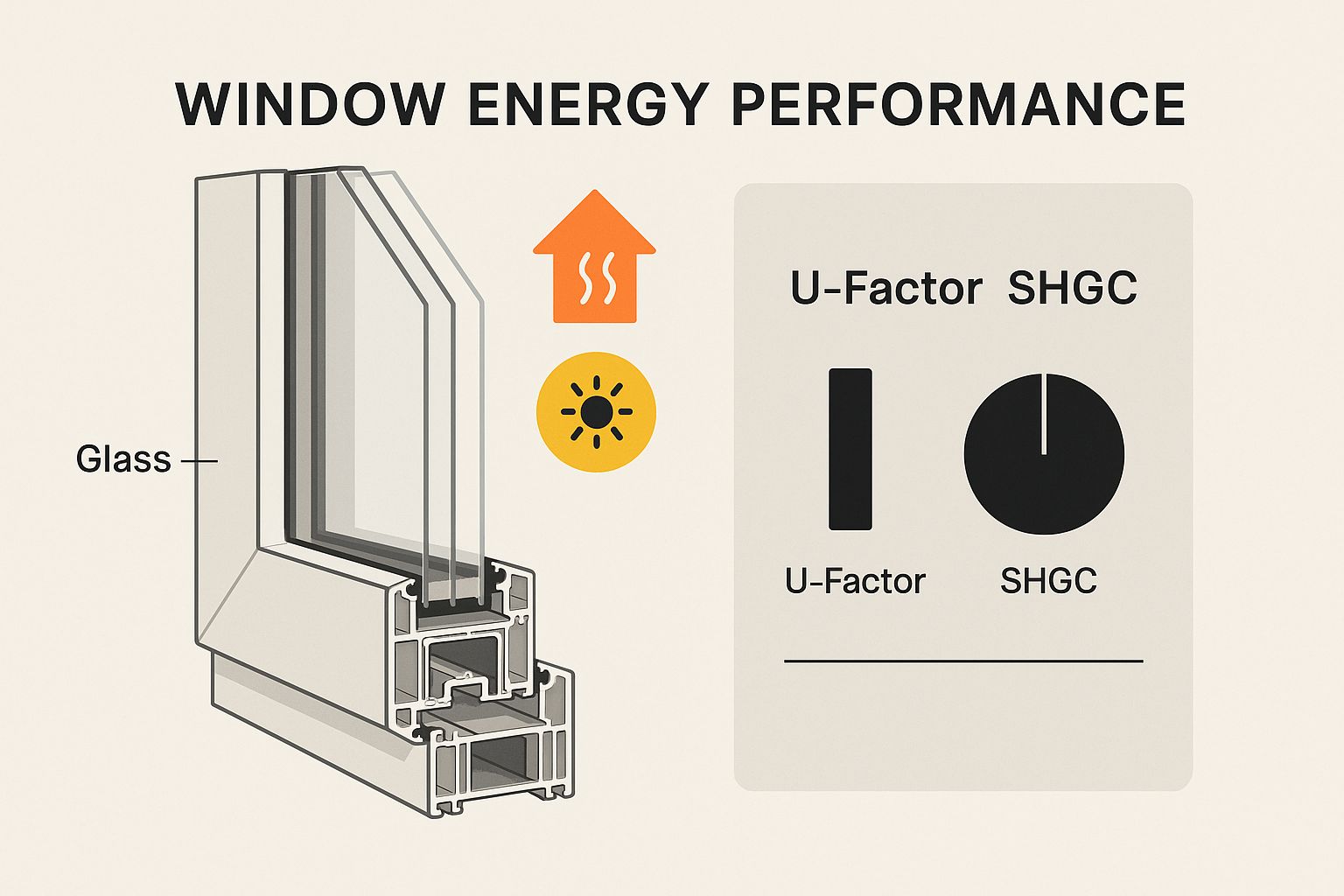
As the infographic illustrates, different window components contribute to overall energy performance. Balancing the U-factor and SHGC is essential for optimal performance in your specific climate. For instance, in colder regions, a low U-factor might take precedence over a low SHGC. You can explore more about window construction and performance at Gladiator Window and Doors.
Decoding Other Important Ratings
Beyond U-factor and SHGC, several other ratings play a significant role. Visible Transmittance (VT) measures the amount of visible light transmitted through the window. A higher VT allows more natural light, potentially reducing the need for artificial lighting. Air Leakage (AL) measures air infiltration through cracks in the window assembly. A lower AL enhances energy efficiency and improves comfort. Finally, Condensation Resistance (CR) indicates a window's ability to resist condensation buildup. A higher CR helps prevent moisture problems and potential mold growth.
To help clarify these metrics, let's look at the following table:
Key Window Energy Efficiency Metrics Explained: A comprehensive breakdown of the primary window efficiency ratings, what they measure, and their importance for different climates.
| Rating Metric | What It Measures | Ideal Values | Importance By Climate |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-factor | Heat transfer through the window | Low (e.g., 0.20-0.30) | More critical in cold climates |
| SHGC | Solar heat gain | Low (e.g., <0.40) in hot climates, moderate (e.g., 0.40-0.60) in mixed climates | More critical in hot climates |
| VT | Visible light transmission | Moderate to high depending on daylighting needs | Important in all climates |
| AL | Air leakage | Low (e.g., <0.30) | Important in all climates |
| CR | Condensation resistance | High (e.g., >50) | Important in humid climates |
As shown in the table, understanding each metric and its ideal values helps you select windows best suited to your needs and location.
Energy efficiency ratings are invaluable tools for consumers and builders alike. The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) provides labels with standardized ratings like the U-factor, facilitating comparisons between different window products. The ENERGY STAR program further certifies windows based on energy performance criteria. These ratings are increasingly important for building code compliance and achieving sustainability certifications. The growing emphasis on thermal efficiency is reflected in the expanding global market, projected to reach about £13,662.24 million by 2026, as reported by GreenMatch.
Choosing the Right Ratings for Your Needs
Prioritizing the right metrics depends on your climate and specific needs. In hot, sunny climates, a low SHGC is crucial to reduce cooling costs. Conversely, in colder climates, a low U-factor for better insulation takes precedence. In climates with both heating and cooling needs, balancing U-factor and SHGC is key. Skylights also require consideration of energy performance. Factors like window orientation and shading also influence the impact of these ratings. West-facing windows, for example, receive more direct sunlight and might benefit from a lower SHGC, even in cooler regions. By understanding these factors, you can select windows that optimize both energy efficiency and comfort.
Navigating Global Window Certification Standards
Choosing energy-efficient windows involves more than simply understanding the U-factor (a measure of heat transmission) and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) (a measure of how much solar heat passes through the window). It means navigating a world of certifications that differ significantly across the globe. This can be a real challenge for homeowners looking to make well-informed decisions. Let's break down the major certification programs and how they can help guide your window selection.
Understanding ENERGY STAR and Other Regional Programs
ENERGY STAR is arguably the most recognized energy efficiency certification for windows in North America. It indicates that a product meets or surpasses specific energy performance standards established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. But ENERGY STAR isn't the only program to consider.
Many regions have their own standards, like the Canadian CSA A440 standard. Some Canadian window and door manufacturers who meet this standard display it proudly on their product literature. Understanding these regional programs ensures you select windows that comply with local requirements and optimize energy savings for your climate.
Decoding Passive House Standards
The Passive House standard, which originated in Germany, takes a demanding approach to building energy efficiency. Windows are essential for achieving Passive House certification. They must satisfy rigorous criteria for U-factor, SHGC, and airtightness.
While not as prevalent as ENERGY STAR, Passive House certification holds considerable value, signifying exceptional energy performance. Opting for Passive House certified windows can dramatically reduce heating and cooling needs, particularly in challenging climates. You might find this helpful: How to master window selection.
Comparing International Certifications
Window certifications extend beyond North America and Europe. Countries like Australia have programs like the Window Energy Rating Scheme (WERS). WERS uses a star rating system to denote a window's energy efficiency, simplifying product comparisons for consumers. The British Fenestration Rating Council (BFRC) in the UK offers a similar rating system. Familiarizing yourself with these international variations helps you compare products from diverse manufacturers and countries, ensuring a fair comparison.
The Importance of Local Building Codes
Window certifications frequently intersect with local building codes. Some codes dictate minimum energy performance levels for windows in new construction or renovations. These codes may reference specific certification programs like ENERGY STAR or set their own performance benchmarks.
Understanding how these codes impact your project is crucial for compliance and avoiding expensive rework. Furthermore, some municipalities offer rebates or incentives for installing certified energy-efficient windows. This can improve the return on investment when you choose high-performance products. By grasping the connection between certifications and local regulations, you can optimize your window selection for both performance and value.
Tomorrow's Windows: Innovation Transforming Efficiency

The world of window energy efficiency is constantly improving. New technologies offer better performance and reshape how we think about windows. These advancements aren't just about better insulation. They're about creating windows that actively contribute to a home's energy production.
Thin Triple Glazing and Dynamic Smart Glass
One exciting development is thin triple glazing. This technology provides the insulation of triple-pane windows without the extra weight and bulk. This makes them easier to install and use, especially in older homes. Dynamic smart glass is another notable innovation. This glass automatically changes its tint based on sunlight. This optimizes natural light and minimizes heat gain. Imagine a window that automatically shades itself on a hot day, keeping your home cool without blinds or curtains.
Vacuum Insulated Glass and Integrated Photovoltaics
Emerging technologies are pushing the boundaries even further. Vacuum insulated glass uses a vacuum between panes for exceptional insulation. This technology achieves significantly lower U-factors than traditional windows, dramatically reducing heat loss. Perhaps the most groundbreaking development is integrating photovoltaics into windows. These windows generate electricity from sunlight. This turns them from energy consumers into energy producers. This offsets a home's energy use and can contribute to the power grid. As window technology improves, it's important to consider how small material changes, like these eco-friendly swap-outs, can improve efficiency and sustainability.
To help understand the differences between these technologies, let's take a look at the following comparison:
Window Efficiency Technology Comparison
Comparison of different window technologies and their efficiency ratings, costs, and performance benefits
| Window Type | Typical U-Factor Range | Approximate Cost Premium | Energy Savings Potential | Best For Climate Zones |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double-Pane | 0.25-0.50 | Baseline | Moderate | 3-8 |
| Triple-Pane | 0.15-0.30 | 10-20% over double-pane | High | 1-7 |
| Thin Triple-Glazing | 0.18-0.25 | 5-15% over double-pane | High | 1-7 |
| Vacuum Insulated Glass | 0.07-0.12 | 50-100% over double-pane | Very High | 1-8 |
| Photovoltaic Windows | 0.20-0.35 | 100-200% over double-pane | Very High (plus electricity generation) | 2-7 |
This table highlights the potential benefits of newer window technologies. While some, like vacuum insulated glass, offer superior insulation, they come at a higher cost. Others, like thin triple glazing, provide a balance of performance and affordability.
Adoption Trends and Investment Considerations
The global market for energy-efficient windows is growing rapidly. Driven by rising energy costs and stricter regulations, the market was valued at USD 21.32 billion in 2023. It's projected to reach USD 43.69 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 8.3%. This reflects a global shift toward sustainability. Regulations like the UK's Future Homes Standard, requiring triple glazing in new homes from 2025, are accelerating this shift. You can find more detailed market statistics here.
In the U.S., the 2024 ENERGY STAR Most Efficient criteria requires stricter U-factor and SHGC ratings. This makes triple glazing important in many climate zones. This trend is expected to continue. Triple glazing is projected to capture over 20% of the U.S. residential market by 2030, up from the current 3%. Explore our window products for more options.
Not all innovations are equal. Some offer real improvements, while others offer marginal gains. It’s important to evaluate these advancements carefully. Consider factors like climate, home design, and budget. By understanding the long-term benefits and drawbacks, homeowners can make informed choices. These choices will improve their home's energy efficiency and comfort.
Matching Window Performance to Your Climate Zone
The perfect window for a sun-drenched home in Phoenix is vastly different from one designed for snowy Minneapolis. Selecting the right window for your climate is essential for optimal energy efficiency and comfort. Let's explore how to choose windows tailored to your specific climate challenges.
Prioritizing U-Factor in Northern Climates
In colder climates, minimizing heat loss is crucial. This is where the U-factor becomes a vital window energy efficiency rating. The U-factor measures how effectively a window insulates against heat transfer. A lower U-factor signifies better insulation. Imagine it like a winter coat – the lower the U-factor, the warmer your house will remain. In northern regions, prioritizing a low U-factor is often more critical than other ratings, helping to reduce heating costs and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature during harsh winters.
The Importance of SHGC in Southern Climates
For homes in hot, sunny climates, controlling solar heat gain is paramount. The Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) measures how much solar heat passes through the window. A lower SHGC translates to less heat entering your home. This is especially important in southern climates where intense sun can lead to overheating. Prioritizing a low SHGC keeps interiors cooler, reducing reliance on air conditioning and lowering energy bills.
Balancing Needs in Mixed Climates
Many areas experience both hot summers and cold winters. In these mixed climates, finding a balance between U-factor and SHGC is key. You'll want a window that insulates well in the winter (low U-factor) and blocks solar heat in the summer (low SHGC). This balanced approach optimizes energy efficiency year-round. For more detailed information, check out this guide: How to Master Window Selection.
Considering Window Orientation and Other Factors
Beyond climate zone, several other factors influence window performance. Window orientation is a major consideration. West-facing windows, for instance, receive significantly more direct sunlight than north-facing windows. This means that even in cooler climates, west-facing windows could benefit from a lower SHGC to manage the afternoon sun.
Tree coverage and architectural features also affect window performance. Trees offer shade, minimizing solar heat gain. Overhangs and awnings can similarly reduce direct sunlight. These elements interact with your window's energy efficiency ratings, impacting its overall performance.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
One frequent mistake is focusing solely on U-factor or SHGC and overlooking other essential ratings such as Visible Transmittance (VT) and Air Leakage (AL). VT measures how much natural light enters through a window, while AL measures air infiltration. Both these factors impact both comfort and energy efficiency.
Another oversight is neglecting the importance of proper installation. Even the highest-performing windows won't function optimally if installed incorrectly. Proper sealing and insulation are crucial for reaping the full benefits of energy-efficient windows. By considering all these elements and avoiding common mistakes, you can choose windows that provide both comfort and substantial energy savings all year long.
The True ROI of High-Performance Windows
Investing in energy-efficient windows is often touted as a smart way to save money on utility bills. But how much truth lies behind this common claim? This section explores the financial realities of replacing windows, examining the factors that can significantly impact your return on investment.
Factors Affecting Payback Periods
Several variables influence how quickly you'll recoup the cost of new windows. Local energy costs are a major factor. If you live in an area with high energy prices, you're likely to see a faster return compared to someone in a region with lower costs.
The quality of the installation is just as crucial. A poor installation can negate the benefits of energy-efficient windows, leading to air leaks and diminished savings. Make sure you choose a reputable installer with a proven track record.
The condition of your existing windows also comes into play. If your current windows are old and drafty, upgrading to high-performance windows will yield more noticeable savings. The worse your existing windows perform, the greater the improvement and the quicker the return.
Understanding the Financial Benefits
While energy savings often take center stage, several other financial perks are often overlooked. Improved comfort is a significant advantage. Energy-efficient windows help maintain a more consistent indoor temperature, reducing drafts and cold spots. This added comfort can create a more pleasant living space and potentially increase your property value.
Reduced HVAC wear and tear is another hidden benefit. With less strain on your heating and cooling system, you may experience fewer repairs and extended equipment lifespan. This translates into substantial long-term savings.
High-performance windows can also decrease fading of furnishings by blocking harmful UV rays. This helps preserve the look of your furniture, carpets, and artwork, delaying the need for costly replacements.
Evaluating Return on Investment
Not all window upgrades deliver equal financial returns. Some upgrades, like switching from single-pane to double-pane windows, typically offer quicker returns due to the considerable improvement in insulation. Other upgrades, such as moving from double-pane to triple-pane, may have longer payback periods depending on climate and energy costs. Check out our guide on How to master window selection for more information.
It's important to have realistic expectations about the payback timeline. Some window upgrades might never fully pay for themselves solely through energy savings, especially in milder climates. However, considering the additional benefits of increased comfort, reduced HVAC wear, and enhanced property value, the overall return becomes much more appealing.
Making Informed Decisions
Before purchasing new windows, conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis. Consider your local energy costs, the condition of your existing windows, and your overall financial goals. A comprehensive evaluation helps you make smart choices aligned with your budget and expectations. While energy savings are a crucial factor, remember to consider the additional benefits that contribute to a more comfortable and valuable home.
Ready to upgrade your home with high-quality, energy-efficient windows and doors? Visit Gladiator Window and Doors today to browse our extensive selection of custom-made products, including extra-large sliding doors, pivot doors, bi-fold doors, panoramic doors, folding windows, and fully loaded pergolas. We offer the lowest prices in the USA, guaranteed with our Best Offer Guarantee. Experience superior craftsmanship, the best warranty in the industry, and unbeatable value.