Why Window Energy Efficiency Ratings Matter Now

Window energy efficiency ratings are more than just stickers. They offer crucial insights into potential cost savings and home comfort. These ratings directly affect your energy bills and how your home feels. For instance, inefficient windows can cause drafts, uneven temperatures, and higher energy use. Understanding these ratings is vital for every homeowner.
The Real Impact of Energy-Efficient Windows
Many homeowners who upgrade to energy-efficient windows see substantial savings on their utility bills. This is a real benefit, confirmed by building science professionals. Energy-efficient windows also improve comfort by minimizing drafts and maintaining stable temperatures throughout the year. The result is a healthier, more comfortable living space.
The growing focus on sustainability globally has profoundly affected the window market. The global energy-efficient windows market, valued at approximately USD 21.32 billion in 2023, is predicted to reach about USD 43.69 billion by 2032. It's expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.3%. This growth stems from increased environmental awareness and stricter building codes aimed at reducing carbon emissions. For more statistics, visit: https://straitsresearch.com/report/energy-efficient-windows-market This trend highlights the increasing importance of energy efficiency in construction.
Shifting Priorities in the Housing Market
Growing environmental awareness has changed what consumers want. Property developers recognize the growing importance of window performance as buyers prioritize eco-friendly features. Window energy efficiency ratings are now key factors in purchasing decisions. They are a major selling point in today's housing market. You might also find this helpful: Our blog sitemap
Initiatives like the UK's Future Homes Standard requiring triple glazing in new homes from 2025 demonstrate a major shift in the industry. Similar regulations in Europe and North America emphasize the global focus on energy-efficient building practices. This highlights the continued development of building codes and how critical window energy efficiency ratings are for meeting these evolving standards.
Mastering the Metrics: U-Factor and SHGC Decoded
Those cryptic numbers on window energy efficiency ratings actually hold the key to a more comfortable and energy-efficient home. Two crucial metrics stand out: the U-factor and the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). Understanding these values empowers you to make informed decisions about your windows.
Understanding U-Factor: Your Window's Insulation Powerhouse
The U-factor measures how well a window prevents heat from escaping your home. Think of it as insulation for your windows – the lower the U-factor, the better the insulation. For example, a window with a U-factor of 0.25 performs much better than one with a U-factor of 1.0. This lower value means less heat escapes during winter, keeping your home warmer and reducing heating bills. Conversely, in the summer, a low U-factor helps keep your home cooler by preventing heat from entering.
Decoding SHGC: Managing Solar Heat
The SHGC measures how much solar heat passes through your window. This is especially important for managing temperature and energy use in warmer climates. A lower SHGC means less solar heat enters your home, reducing cooling costs in the summer. However, a higher SHGC can be beneficial in colder climates, allowing sunlight to passively heat your home during winter. The ideal SHGC depends on your climate and window orientation. When considering window efficiency, you may also want to consider skylights. Learn more about the energy efficiency of skylights.
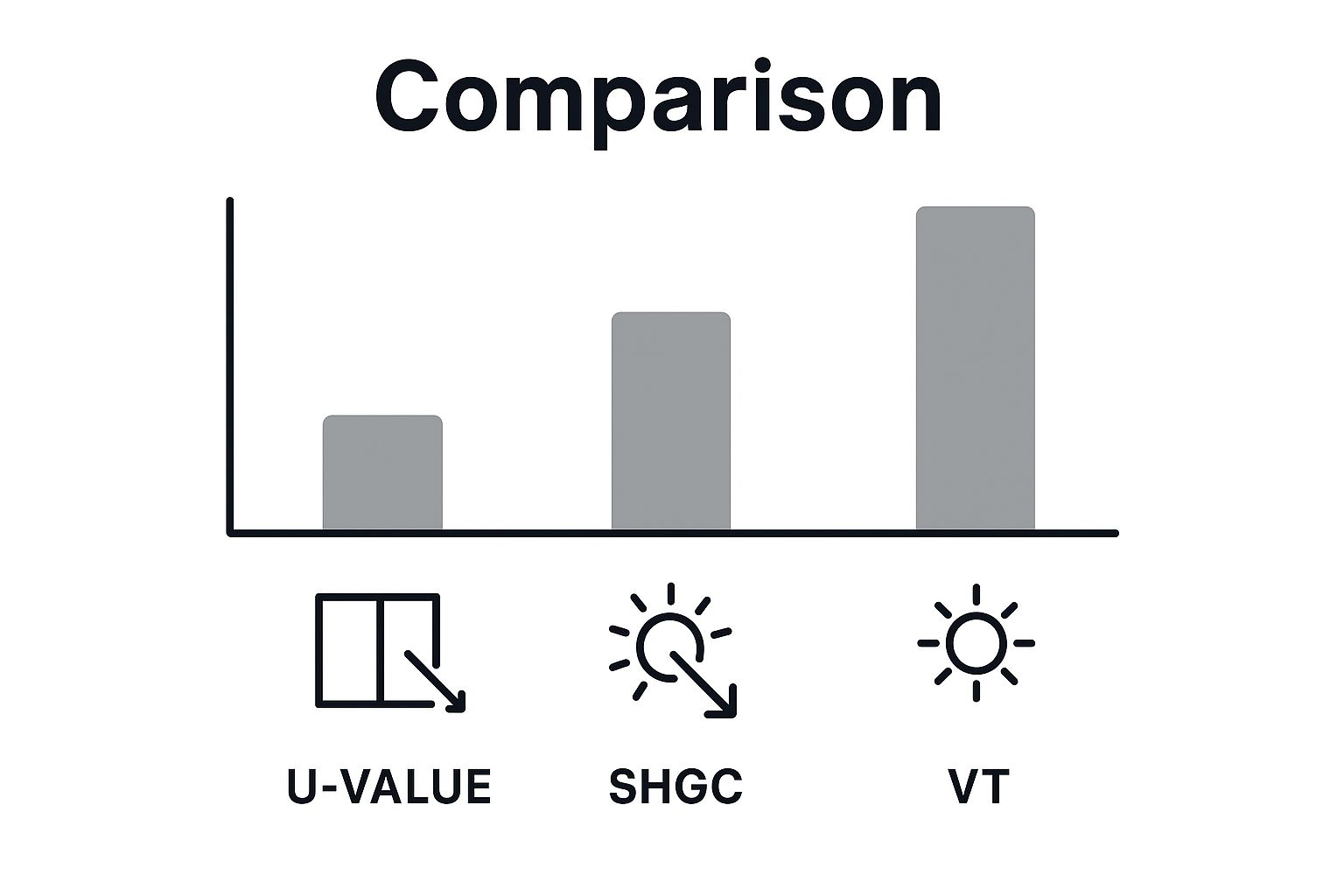
The infographic above illustrates the relationship between U-factor, SHGC, and Visible Transmittance (VT). Balancing these three factors is crucial for optimizing both energy efficiency and natural light. Ideally, you want lower U-factor and SHGC values while maintaining good VT.
To further understand these metrics, let's look at a comparison table:
To help illustrate these concepts, the following table provides a comparison of key window energy efficiency metrics.
Window Energy Efficiency Metrics Comparison A comprehensive comparison of key window energy efficiency metrics across different rating systems and their impact on energy performance
| Metric | What It Measures | Ideal Values | Climate Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Factor | How well a window prevents heat transfer | Lower is better (e.g., 0.20-0.30) | Crucial in cold climates for heat retention, important in hot climates to prevent heat gain. |
| SHGC | How much solar heat passes through a window | Depends on climate – lower for hot climates (e.g., <0.40), higher for cold climates (e.g., >0.40) | Important in hot climates for reducing cooling load, can contribute to passive heating in cold climates. |
| VT | How much visible light passes through a window | Higher is generally better for daylighting, but balance with SHGC to avoid glare and overheating | Important for maximizing natural light and reducing the need for artificial lighting. |
This table highlights the importance of considering climate when selecting windows. For example, while low U-factors are always desirable, the ideal SHGC will vary based on location.
Balancing the Metrics for Optimal Performance
Choosing the right U-factor and SHGC depends largely on your climate. In colder regions, a low U-factor is paramount for heat retention. In hotter climates, a low SHGC is essential for minimizing unwanted solar heat gain. Energy efficiency in windows relies heavily on these two metrics. In the United States, the 2024 Energy Star Most Efficient criteria have raised the bar, making triple glazing increasingly necessary in several climate zones. This shift towards triple glazing is projected to increase its market share significantly, from around 3% currently to over 20% by 2030. The global insulating glass window market, designed for better thermal efficiency, was valued at approximately £10,139.36 million in 2021 and is expected to reach £13,662.24 million by 2026. More detailed statistics can be found here. You can also learn more about how to master window selection. Carefully balancing these metrics is crucial for maximizing both energy savings and year-round comfort.
Navigating Global Rating Systems Like an Expert

Understanding window energy efficiency ratings is essential. However, these systems can differ significantly around the world. What's considered energy-efficient in one location might not meet the standards of another. This guide will help you understand these international variations so you can confidently compare window products, no matter their origin.
Decoding North American NFRC Labels
In North America, the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) label sets the standard for window energy efficiency. The NFRC provides key performance metrics:
- U-factor: Measures how well a window prevents heat from escaping.
- SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient): Measures how much solar heat passes through the window.
- VT (Visible Transmittance): Measures how much light passes through the window.
A U-factor of 0.30 or lower is generally considered good in most climates. Understanding the interplay of these metrics is crucial for selecting the right window. The NFRC label allows for clear comparisons, empowering informed decisions.
Understanding UK Energy Rating Bands
The UK uses a different approach: a straightforward A++ to G rating scale for window energy efficiency. These bands represent overall window performance, encompassing factors such as U-factor, SHGC, and air leakage. A-rated windows represent the highest efficiency. This visual system makes it easy to quickly understand performance levels. However, these ratings are tailored to the UK's specific climate and building practices.
Comparing European CE Marks and Australian WERS Ratings
The European CE mark signifies that a product meets certain safety and performance standards, including energy efficiency. However, it offers fewer specific performance details than the NFRC label. Australia uses the Window Energy Rating Scheme (WERS), which rates windows using a star rating system. More stars indicate higher efficiency, similar to the NFRC's principles. Both systems aim to improve energy efficiency but differ in their presentation and testing methods. Understanding these nuances is vital for accurate comparison.
Regional Climate Priorities Reflected in Rating Systems
Rating systems often reflect regional climate priorities. Colder climates emphasize the U-factor for insulation, while hotter climates prioritize SHGC for solar heat control. International architects consider these regional variations when selecting windows for projects. This localized approach helps ensure optimal window performance for specific climate conditions.
Practical Translation Tools for Global Comparison
Thankfully, several online resources offer conversion tools and charts for comparing window ratings across different systems. These tools help translate, for example, a European U-value into its North American equivalent. This allows you to compare windows from various manufacturers around the globe. This "apples-to-apples" comparison is critical for making well-informed decisions in today's global market. By understanding these rating systems, you can confidently choose the perfect windows for your needs and climate, regardless of where they are manufactured.
The Technology Behind Top-Performing Windows
What makes a window truly energy-efficient? It's more than just a pane of glass. It's a combination of advanced technologies working together to create a barrier against the elements. This section explores the science behind these innovations, helping you understand what to look for in a high-performing window.
The Science of Glazing: More Than Meets the Eye
Modern window glazing is a feat of engineering. Multiple layers, or panes, of glass are separated by spacers, forming insulating air or gas-filled cavities. These cavities dramatically reduce heat transfer. Furthermore, microscopic metallic coatings, often invisible, are applied to the glass. These low-emissivity (low-E) coatings reflect infrared radiation, further minimizing heat flow.
This combination of multiple panes, gas fills, and low-E coatings works like a high-tech thermos, keeping your home warm in winter and cool in summer. For instance, double-pane windows with low-E coatings and argon gas fills considerably outperform single-pane windows in energy efficiency.
Frame Materials: A Critical Component
The frame material significantly impacts a window’s overall energy performance. Different materials conduct heat at different rates. Aluminum, while durable, is highly conductive. Wood and vinyl offer significantly better insulation.
Each material has its pros and cons related to durability, maintenance, and cost. Hybrid frame materials, combining the strengths of different materials, have recently emerged. These hybrids aim to maximize energy efficiency and structural integrity. For example, some combine wood interiors with aluminum exteriors for weather resistance.
Warm-Edge Spacers: Breaking the Thermal Bridge
Traditional metal spacers can create a thermal bridge, allowing heat to escape through the frame. Warm-edge spacers, made from less conductive materials like foam or rubber, minimize this heat transfer. This seemingly small detail can significantly impact overall energy efficiency, directly contributing to better window energy efficiency ratings. You might be interested in: Learn more in our article about sitemap.
Comparing Glazing Technologies
To understand the impact of different glazing technologies, let's look at the data. The following table compares various glazing types and their effect on energy efficiency.
Glazing Technologies and Their Impact on Efficiency Ratings
Comparison of different glazing technologies showing their typical U-factor and SHGC values along with energy-saving potential
| Glazing Type | Typical U-Factor | Typical SHGC | Annual Energy Savings (estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Pane | 1.0 | 0.85 | - |
| Double-Pane (Clear Glass) | 0.5 | 0.75 | 10-15% vs. single-pane |
| Double-Pane (Low-E & Argon Gas) | 0.3 | 0.4 | 25-35% vs. single-pane |
| Triple-Pane (Low-E & Argon Gas) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 30-50% vs. single-pane |
As the table shows, advanced glazing technologies offer significant energy savings. While the upfront cost might be higher, the long-term savings on heating and cooling make it a worthwhile investment. Understanding these technologies helps you make informed decisions, ensuring your windows meet your aesthetic and energy-efficiency goals.
Choosing Perfect Windows for Your Climate Zone

The perfect window for a Minnesota home might be entirely wrong for a Miami home. Climate significantly impacts window selection, affecting both energy efficiency and comfort. Choosing windows with the right window energy efficiency ratings is crucial. This section will explore how to choose windows tailored to your climate zone.
Optimizing Window Specifications for Diverse Regions
Top builders know how climate impacts window performance. They adjust window specifications according to regional temperatures, sun exposure, and seasonal changes. For instance, homes in hot, sunny areas benefit from windows with low Solar Heat Gain Coefficients (SHGC) to reduce heat. Homes in colder areas may prioritize low U-factors for better insulation. For further information on window and door options, see this article: Learn more in our article about window and door options.
North vs. South: Leveraging Window Orientation
Window orientation plays a key role in energy efficiency. North-facing windows get less direct sunlight, minimizing summer heat gain. These windows should maximize natural light with higher Visible Transmittance (VT) values while maintaining a good U-factor for insulation.
South-facing windows get lots of sunlight. This helps with passive solar heating in winter but requires managing summer heat gain with a lower SHGC.
Balancing Competing Factors in Mixed Climates
Mixed climates pose unique challenges. They experience both hot summers and cold winters, requiring a balance between preventing heat gain and retaining heat. Optimizing window performance here takes a more nuanced approach.
A slightly higher SHGC might help with passive heating in winter, while a moderate U-factor ensures year-round comfort. Passive house designers often use strategies like overhangs or exterior shades to optimize window performance.
Selection Matrices for Different Climate Zones
Choosing windows with the right energy efficiency ratings can be daunting. Simplified selection matrices offer helpful guidance. These matrices suggest U-factor and SHGC ranges for different climate zones. This helps you navigate conflicting advice and choose windows with the ideal ratings for your location, simplifying the process. Understanding your climate and using these guidelines lets you choose windows that maximize energy efficiency, comfort, and long-term savings.
The Real ROI of High-Performance Windows
High-performance windows offer significant long-term value that goes beyond the initial purchase price. This value extends past simple energy savings and includes several key areas that contribute to a substantial return on investment. Let's explore how to calculate this ROI and uncover the comprehensive benefits.
Calculating the Financial Benefits
Evaluating the financial benefits of energy-efficient windows involves several factors. Consider your current windows' performance, your local climate, and your energy costs. High-performance windows, equipped with features like low-E coatings and argon gas fills, significantly reduce energy loss. This translates to lower heating and cooling bills, providing substantial savings over time. For example, upgrading from single-pane windows to Energy Star-certified windows can significantly reduce annual energy consumption.
Looking at real-world examples can help illustrate the potential impact. Homeowners in colder climates often report considerable savings on heating bills after upgrading their windows. Similarly, those in warmer regions experience reduced cooling costs after installing high-performance windows. These real-life scenarios showcase the tangible financial benefits of investing in window energy efficiency.
Incentives and Rebates: Offsetting the Initial Investment
Researching available incentives is a crucial step in maximizing your ROI. Various programs, including federal tax credits and local utility rebates, can significantly offset the upfront cost of high-performance windows. The federal government, for instance, offers tax credits for qualifying energy-efficient home improvements. Many utility companies also provide rebates for upgrading to energy-efficient windows. Knowing about and utilizing these programs can dramatically reduce your overall window upgrade expenses.
Beyond the Dollars and Cents: Comfort and Well-being
The true ROI of high-performance windows extends beyond financial gains. They significantly improve home comfort by reducing drafts and maintaining more consistent indoor temperatures. This enhanced comfort also lessens the strain on your HVAC system, potentially extending its lifespan. Furthermore, high-performance windows can improve indoor air quality by reducing outside noise and pollutants, contributing to a healthier and more peaceful home environment.
Calculating Your Potential Savings
Accurately estimating your potential savings requires considering your unique situation. Fortunately, several online tools and calculators can help. These resources allow you to estimate potential savings based on factors such as your local climate, energy rates, and the performance of your existing windows. Using these tools empowers you to make informed decisions and ensures your window investment delivers the desired returns. By taking the time to calculate your potential ROI, you can confidently invest in windows that offer both financial and lifestyle advantages. Installing energy-efficient windows can also significantly increase home value and contribute to your home's overall worth.
The Future of Window Energy Efficiency Innovation
The world of window technology is constantly evolving, promising exciting advancements in energy efficiency for our homes. Current window ratings may soon become outdated as these innovations take hold. Let's explore what lies ahead.
Dynamic Glazing: Adapting to Changing Conditions
Imagine a window that intelligently adjusts to the weather. Dynamic glazing makes this a reality. Utilizing special materials, these windows change their properties in response to sunlight and temperature. On a scorching summer day, the glass darkens to minimize heat, while on a cloudy day, it becomes transparent to maximize natural light. This offers significant energy savings and increased comfort.
Window-Integrated Solar Collection: Generating Power From Your Windows
Researchers are exploring integrating solar cells directly into window glass. This innovative approach could transform windows from passive components to active energy generators. Although still in early stages, this technology has enormous potential for reducing our dependence on traditional energy sources. Imagine your windows partially powering your home! You might be interested in: Learn more in our article about our blog.
Ultra-Thin Vacuum Glazing: Outperforming Triple Panes
Vacuum glazing uses a vacuum-sealed space between glass panes for superior insulation. This technology can surpass even the best triple-pane windows in performance, while being significantly lighter and thinner. This makes them an attractive option for new construction and renovations alike. Vacuum glazing pushes the limits of energy efficiency, dramatically improving thermal performance. Installing energy-efficient windows can significantly increase home value and boost your home's overall worth.
New Metrics for a New Era
As window technology progresses, so must our methods of measurement. Researchers are developing metrics that go beyond traditional U-factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) ratings. These new metrics will account for the dynamic nature of emerging technologies, providing a more complete understanding of window energy performance. This will enable more accurate comparisons and informed decisions in the future.
Market-Ready vs. Future Developments
Some of these technologies are nearing market availability, while others remain in the research and development phase. Dynamic glazing, for example, is currently available in some applications. However, window-integrated solar cells are still several years away from widespread use. Understanding the timeline of these advancements is essential for making smart window investments.
Regulatory Trends and Climate Change
Climate change and stricter building codes are driving window technology innovation. Governments globally are implementing policies to reduce building energy consumption, resulting in more demanding window performance requirements. This is accelerating the development and adoption of advanced window technologies, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Ready to explore the future of window technology? Upgrade your home with Gladiator Window and Doors, specializing in extra-large sliding doors, pivot doors, bi-fold doors, panoramic doors, and folding windows, as well as fully loaded pergolas. We offer the lowest prices in the USA with our Best Offer Guarantee, providing top-quality, custom-made, thermally rated, and USA-approved products. Visit us today for massive doors at a fraction of the cost!